Babies can start teething as early as 3 months old. Teething typically begins around 6 months.
Teething, the process of a baby’s first teeth emerging, typically starts around 6 months of age, but some babies may begin as early as 3 months. Signs of teething include increased drooling, irritability, and chewing on objects. The bottom front teeth, known as the central incisors, are usually the first to come in, followed by the upper front teeth.
Teething can be a discomforting experience for both the baby and the parents, but there are various remedies and teething toys available to help alleviate the pain and discomfort. Understanding the typical timeline of teething can assist parents in recognizing and addressing the symptoms as they arise.
Early Signs Of Teething, Common Symptoms To Look For
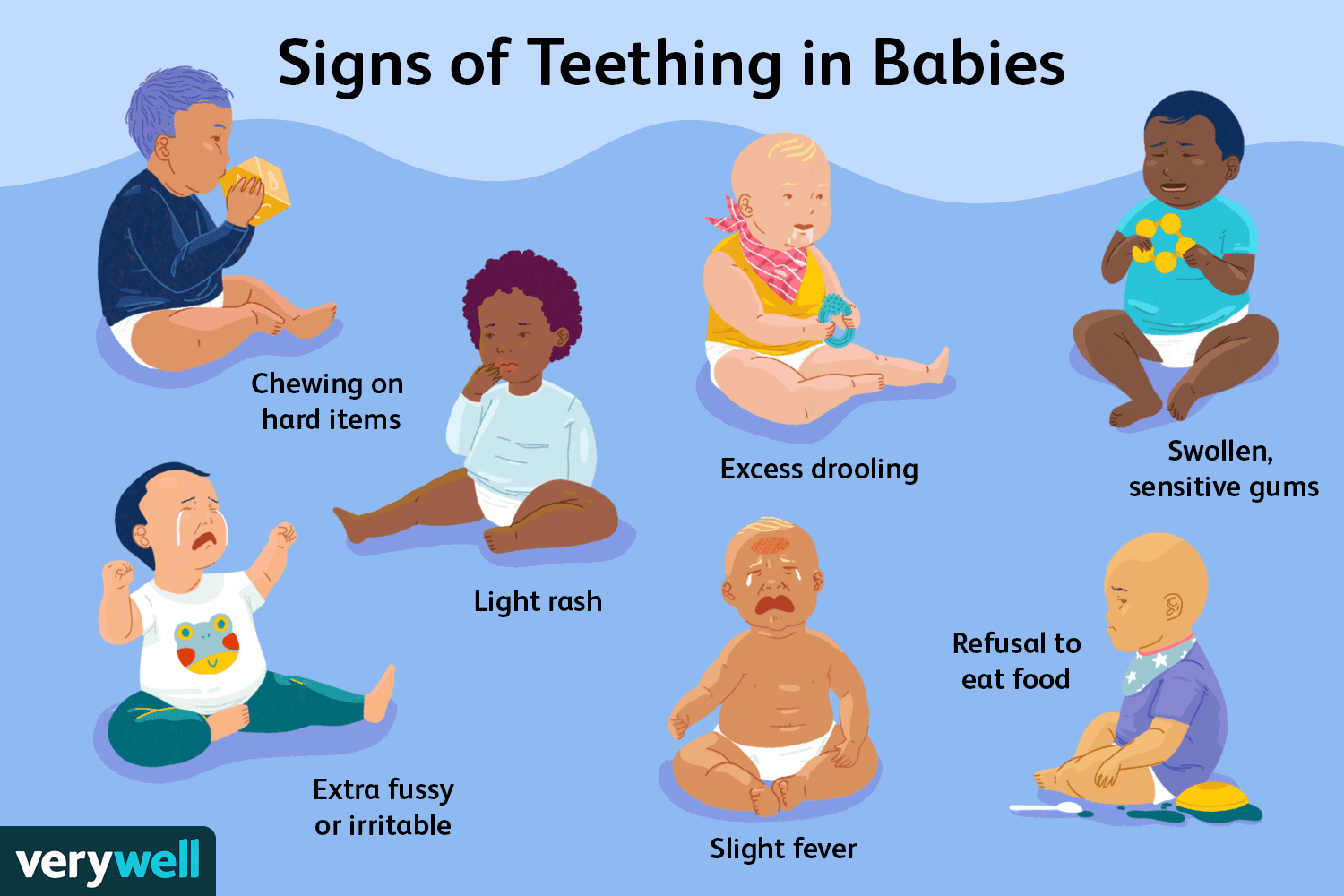
Increased drooling: Your baby may start to drool more than usual as their salivary glands become more active.
Chewing and biting: Babies may chew on their fingers, toys, or other objects to alleviate the discomfort in their gums.
Irritability: Your little one might become fussier than usual due to the soreness and discomfort caused by teething.
Swollen or sensitive gums: The gums may appear red, swollen, or tender to the touch.
Typical Age Range For Teething, babies start teething
Most babies start teething between 4 and 7 months of age, with the lower central incisors often being the first to emerge. However, some infants may begin teething earlier, around 3 months, while others may not start until after their first birthday.
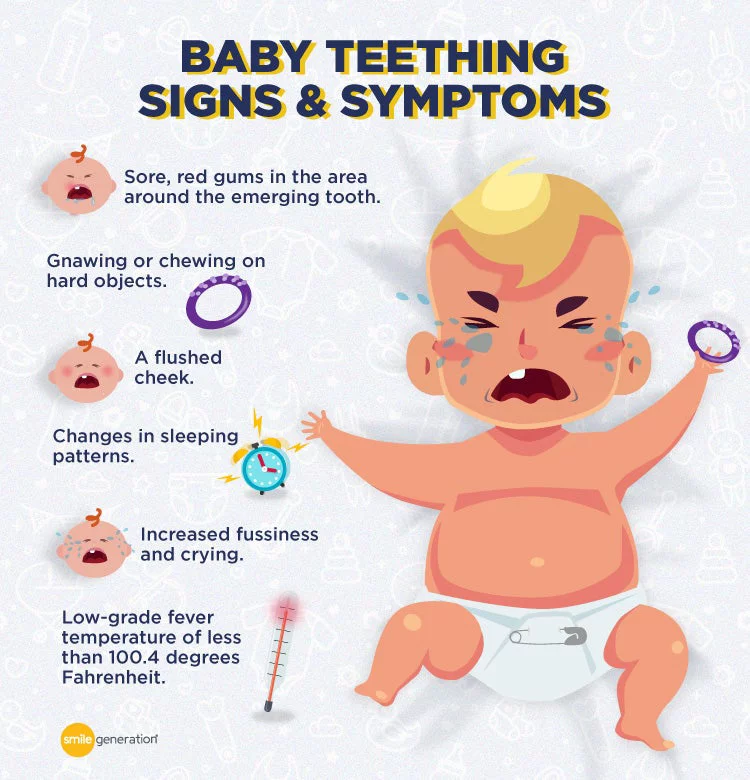
Factors Influencing Early Teething
Teething is a significant milestone in a baby’s development, marking the emergence of their first teeth. While most babies start teething between 4 and 7 months of age, it is not uncommon for some infants to begin the teething process earlier. Several factors can influence early teething, including genetics and family history, as well as preterm birth and low birth weight. Let’s explore these factors in more detail.
Genetics And Family History
The timing of teething can be influenced by genetics and family history. If both parents experienced early teething during their infancy, it is likely that their baby will follow a similar pattern. The genes inherited from the parents play a crucial role in determining when a baby’s teeth start to appear. It is important to note that genetics is not the sole factor at play. Other factors, such as the baby’s overall health, can also impact the teething timeline.
Preterm Birth And Low Birth Weight
Babies who are born prematurely or with low birth weight may experience early teething. Prematurity refers to babies born before 37 weeks of gestation, whereas low birth weight refers to infants weighing less than 2,500 grams at birth. These babies may start teething earlier than their full-term counterparts due to the developmental differences in the formation of their teeth.
Teething can be an exciting albeit challenging time for both babies and their parents. Understanding the factors that can influence early teething can help parents prepare and provide appropriate care for their little ones. While genetics and family history, as well as preterm birth and low birth weight, play a role in early teething, it is crucial to remember that every baby is unique and may follow a slightly different timeline. If you have concerns about your baby’s teething, it is best to consult with a pediatrician or dentist for guidance and support.
Precocious Teething
Teething is a natural developmental process that typically begins when a baby is around 6 months old. However, some babies may experience precocious teething, which refers to the occurrence of teething at an earlier age than usual. In this article, we will explore the definition and criteria of precocious teething, as well as potential risks and concerns associated with this phenomenon.
Definition And Criteria
Precocious teething, also known as early teething, is when a baby’s first tooth erupts before the age of 4 months. While it is considered normal for teeth to start appearing around 6 months, every child is unique, and a few may begin the teething process much earlier. Experts generally consider precocious teething if the first tooth erupts between 3 and 4 months of age.
However, it’s important to note that the timing of teething can vary from one baby to another. Some infants may have their first tooth as early as 3 months, while others may not show any signs of teething until after 6 months. Therefore, it is essential to consider other factors alongside the age, such as the presence of typical teething symptoms and the eruption pattern of multiple teeth.
Potential Risks And Concerns
While precocious teething may seem like an exciting milestone, it is crucial for parents and caregivers to be aware of the potential risks and concerns associated with early teething. Here are some factors to consider:
- Dental Development: Early teething does not necessarily indicate advanced dental development. It is possible for a baby to have their first tooth early but still follow a normal eruption pattern for other teeth.
- Nutrition and Digestion: Babies who begin teething earlier may experience challenges with breastfeeding or bottle feeding. The discomfort or pain caused by teething can affect their ability to latch properly, leading to feeding difficulties.
- Choking Hazard: If a baby starts teething before they develop sufficient motor skills, they may be more prone to choking on toothbrushes, teething toys, or other objects they put in their mouth to alleviate discomfort. Vigilance is crucial during this period to ensure their safety.
- Speech and Language Development: Early teething can impact the development of speech and language skills. Babies who begin teething before their mouth muscles are adequately developed may face difficulties in articulation and pronunciation.
- Early Tooth Decay: The eruption of teeth at an earlier age could increase the risk of tooth decay. It is essential to establish good oral hygiene habits early and monitor the baby’s oral health carefully.
Remember, each baby’s teething journey is unique, and while precocious teething might require a bit of extra attention, it is not necessarily a cause for alarm. Keeping a close eye on your baby’s oral health and consulting with a pediatric dentist can help ensure their teeth and overall development are on track.
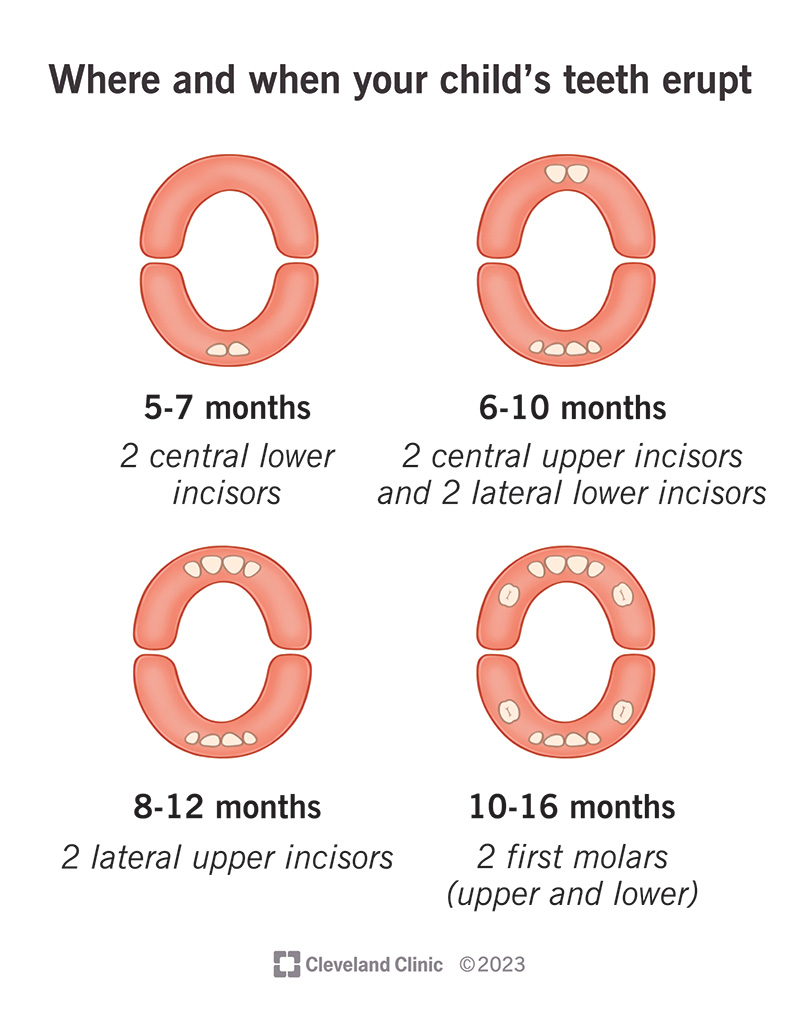
Difference Between Early And Normal Teething
Teething is an important milestone in a baby’s life, but did you know that some babies may start teething earlier than others? While the average age for teething to begin is around six months, it is also considered normal for babies to start teething anywhere between three and twelve months of age. This leaves a wide window of time for babies to begin this process. However, there are some key differences between early and normal teething that parents should be aware of.
Developmental Milestones
Early teething is often associated with other early developmental milestones. These babies may start rolling over, sitting up, or crawling earlier than their peers. On the other hand, babies who experience teething at the average age tend to follow a more regular pattern of development. It’s important to remember that every baby is unique, and reaching developmental milestones at different times does not necessarily indicate a problem. However, it can be helpful for parents to monitor their baby’s progress and consult with a healthcare professional if they have any concerns.
Impact On Oral Health
Early teething can have both positive and negative impacts on a baby’s oral health. On one hand, early teeth eruption can provide infants with new opportunities to explore their mouths, which is crucial for oral sensory development. It can also help in the introduction of solid foods, as the baby can chew and mash them with their new teeth. However, early teething can also lead to potential challenges. These may include increased discomfort and irritability for the baby, as their gums may be more sensitive. It’s important for parents to be proactive in providing soothing measures, such as teething rings or cool washcloths, to alleviate any discomfort their baby may experience.
Management Strategies For Early Teething
When it comes to managing early teething in babies, parents can employ various strategies to alleviate discomfort. These strategies focus on providing comfort to the baby and consulting healthcare providers when necessary.
Comfort Measures
- Gently massaging the baby’s gums with a clean finger or soft cloth can help soothe teething pain.
- Offer a chilled teething ring or cold washcloth for the baby to gnaw on to numb the gums.
- Ensure the baby has adequate distractions and toys to divert attention from teething discomfort.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
- If teething symptoms are severe or persistent, seek advice from a pediatrician or dentist.
- Discuss the possibility of using safe teething remedies recommended by healthcare professionals.
- Monitoring the baby’s overall health and development during teething is crucial for proper management.
Teething Myths And Facts
Common Misconceptions
Myth: Babies start teething at six months old.
Fact: Teething can begin as early as three months.
Scientifically Proven Information
Myth: All babies experience teething discomfort.
Fact: Not all babies exhibit signs of teething discomfort.
Caring For Early Teething Babies
Babies can start teething as early as three months old, although the average age is around six months. Early teething can be challenging for both the baby and the parents, as the little one may experience discomfort and irritability. Caring for early teething babies involves implementing oral hygiene practices and choosing safe teething products to ensure their comfort and well-being.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Oral hygiene for early teething babies is crucial to prevent discomfort and maintain their overall health. Gently wipe the baby’s gums with a clean, damp cloth after feedings to remove bacteria and residue. As the baby’s teeth start coming in, transition to using a soft-bristled baby toothbrush suitable for infants, and introduce a non-fluoride toothpaste. Regularly cleaning the baby’s mouth helps establish good oral hygiene habits from an early age.
Choosing Safe Teething Products
When selecting teething products for early teething babies, it is important to opt for safe and effective options. Silicone teething rings and teething toys, specifically designed for infants, can provide relief for the baby’s sore gums. Ensure that the chosen products are free from harmful chemicals and meet safety standards. Additionally, refrigerated teething toys can offer soothing relief for teething discomfort.

Can A 2 Month Old Be Teething?
Yes, it’s possible for a 2-month-old to start teething. Symptoms may include drooling, irritability, and chewing on objects. Always consult a pediatrician for confirmation and guidance on teething remedies.
How Do I Know If Baby Teething?
You can tell if your baby is teething by increased drooling, chewing on objects, crankiness, and swollen gums.
Why Is My 2 Month Old Drooling And Chewing On Hands?
Drooling and chewing hands is normal at 2 months as your baby is exploring sensory experiences.
What Does First Stage Of Teething Look Like?
During the first stage of teething, babies may exhibit symptoms like increased drooling, irritability, swollen gums, and a desire to chew on objects.
Conclusion
Teething can begin as early as 3 months of age, but every child is different. It’s important for parents to be aware of the signs and symptoms of teething and to provide appropriate care and comfort to their babies during this stage.
Stay informed, patient, and supportive as your little one goes through this natural process.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/at-what-age-will-my-baby-start-teething-5085119_text-6f827b0d6c184a3f9cc934cf101596c2.png)